What is a Cholesteatoma?
Cholesteatoma is a skin growth that occurs in the middle ear behind the eardrum. The patient may experience ear pain, fullness of the ear, dizziness or weakness on the effected side of the face. Depending on the size of the cholesteatoma, treatment can include antibiotics and eardrops or surgery may be necessary to remove the growth. Various tests may be needed such as, hearing and balance testing or CT scans.
What Causes Cholesteatoma?
When the eustachian tube is functioning normally, it equalizes ear pressure by moving air from the back of the throat into the middle ear. Allergies and viruses can impair this process, leading to a partial vacuum in the ear.
Negative pressure stretches the eardrum, creating a pocket or cyst that fills with old skin cells which can become easily infected. In rare cases, the cholesteatoma can be congenital (present at birth).
What Are the Symptoms of Cholesteatoma?
Symptoms of cholesteatoma include drainage from the ear, a feeling of fullness, hearing loss, earache and dizziness. Since these symptoms are also present in other conditions, tests such as audiograms and CT scans can rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis. Cholesteatomas continue to grow if not treated and can lead to complications such as:
- Deafness
- Facial paralysis
- Brain abscess
- Meningitis
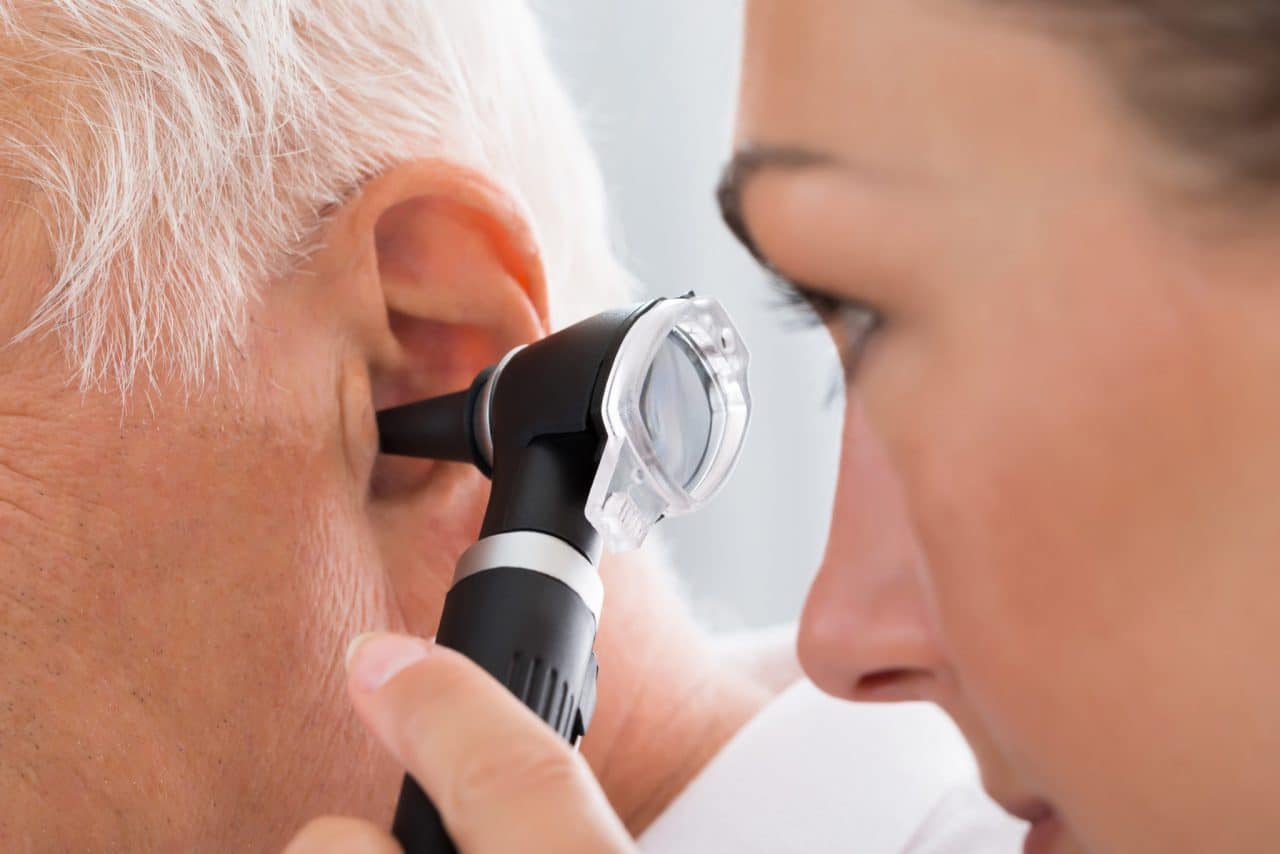
How Is a Cholesteatoma Diagnosed?
A cholesteatoma diagnosis typically begins with a medical history and visual inspection with an otoscope. An audiogram or tympanogram hearing test can help determine the level of hearing loss, and a CT scan of the temporal bone may be ordered. Some of the symptoms that can lead a physician to suspect a cholesteatoma include:
- History of past middle ear infections or fluid buildup
- Discharge from the ear
- Gradual loss of hearing
Call Western Michigan ENT at (231) 398-9536 for more information or to schedule an appointment.